Qwertyman for Monday, February 23, 2026
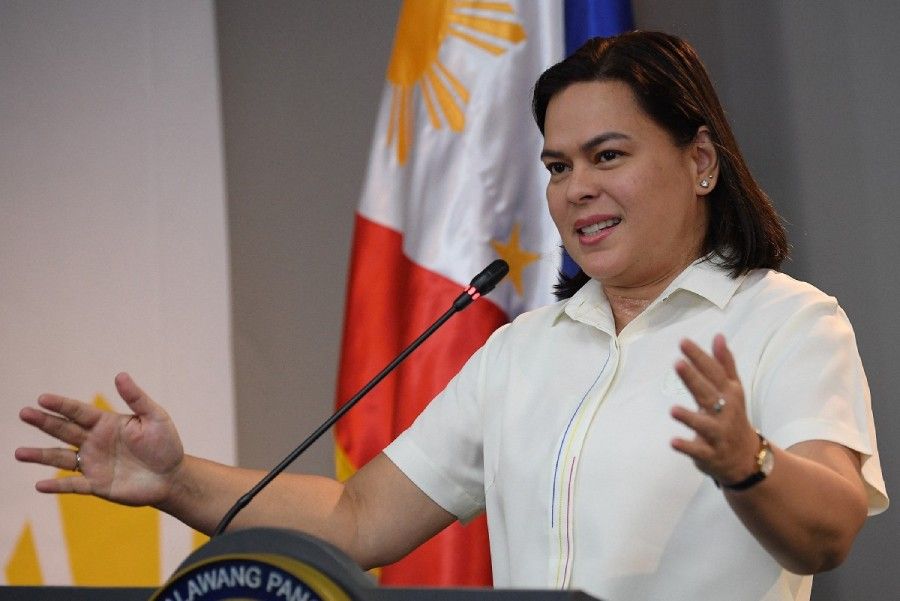
TO NO one’s great surprise—except perhaps for the “why now”—Vice President Sara Duterte publicly announced last week her plan to run for president in 2028.
I’ll leave the more informed and more nuanced readings of this event to the professional analysts, but from my pedestrian point of view, the timing’s the thing. By throwing down the gauntlet so early, more than two years before the actual election, VP Sara is leaving no doubt as to her intentions (which we all knew, already).
It doesn’t take a PhD in Political Science to see that, more importantly, with her impeachment being revived in the House, presumably to be raised to the Senate, she is serving notice to our notoriously opportunistic politicos that they better fall in step now—or else. The Dutertes still hold sway over vast swaths of political territory especially in the south, where pro-impeachment legislators can be easily picked off and punished in a Duterte restoration. When it comes down to a vote, the math will tell the story of who’s afraid of Sara Duterte.
The question really is, what are we progressive-minded citizens and our leaders supposed to do?
Right now, the DDS side has one advantage over everyone else. It’s fighting for its life, with whatever power and influence it retains. With its patriarch in prison and his successor in peril for her political future, it has to go all-in on Sara’s candidacy or face even greater and perhaps permanent debilitation. That gives it a clarity of purpose that’s easier to translate to specific actions, to a tight script and playbook, than it is for the yet amorphous, once improbable, and still highly hypothetical Pinklawan-administration united front to agree on the most basic terms of coalition.
I can sense the hand of AI in fleshing out the details of the aforementioned script, but as one recent DDS post puts it, here’s the winning scenario:
“…. A story, the kind of story that does not need advertising, does not need media allies, does not need oligarch money, because it tells itself. A father who loved his country enough to die for it in a foreign prison. A daughter who loved her father enough to fly across the world to sit with him in chains. A people who loved them both enough to wait, and watch, and when the moment came.. to roar!!!
“The grandmaster played his greatest game not from the presidential palace. Not from the campaign trail. Not from a position of power and comfort.
“He played it from a cell. With nothing but his mind, his daughter, and his unbroken faith in the Filipino people.
“And when Sara Duterte raises her right hand in 2028 when the Philippines renders its verdict on everything that has happened, everything that was done to them, everything they endured and refused to surrender — Rodrigo Duterte will not be there to see it. Or maybe he will, we do not know.
“But he will have made it happen.”
I commented on this post by saying “I wonder what the AI prompt was,” because it displays the kind of verbal cadence, the dramatic buildup employing sentence fragments, the repetition for emphasis, so common to AI-assisted compositions.
But AI or not, it does create the kind of simple but spinnable story that appeals to soft-minded and soft-hearted voters, drawing on a long and deep Pinoy tradition of melodrama that sanctifies the api, the unjustly oppressed. The day before Sara’s announcement, Digong had played his part by casting himself in a letter to the International Criminal Court as a man “old, tired, and frail,” prepared to “die in prison” with his “heart and soul (always remaining) in the Philippines.”
Those of us who know better lost no time pointing out the hypocrisy of the old man’s demand for the “respect” he never showed his political enemies and tokhang victims, and we can all go to sleep convinced of his guilt and wishing for his expectation to be realized. But the truth, in a sense, is almost irrelevant now in what will be a war of narratives, which Sara hopes to win.
From her side of the story, her father is already lost—and therein lies his political value, as sacrificial martyr, which can only rise should he in fact perish in prison or appear even more “old, tired, and frail” closer to 2028. Her impeachment, if it happens, will also amplify her kaapihan. Her disqualification from running for public office will require another step—a separate vote in the Senate, as far as I know (do correct me if I’m wrong)—or at least a separate and possibly concurrent criminal conviction. She could also resign before impeachment, surfacing the unresolved question of whether she can still be impeached and disqualified after. Clearly, if the point is to appear at a constant disadvantage to project persecution, Sara will not want for options.
And she shouldn’t, because if we believe in her guilt as much as we do in her father’s, then the only way forward is forceful prosecution, the awa factor be damned. Criminal convictions for both will provide a definitive conclusion. But on the safe assumption that nothing in this country, including some Supreme Court decisions, is ever truly final, it remains possible that Sara Duterte will be on the ticket in 2028.
Whatever kind of opposition emerges to contest the DDS will need a powerful counter-narrative to the Sara saga—which, I suspect, will wear thin as the evidence of criminal wrongdoing piles up against the Dutertes at the Hague and in Manila.
An ascendant story could emerge from someone who has her own underdog story to tell—of being diminished and marginalized in Digong’s regime, but of serving nobly nonetheless—and, more significantly, of keeping herself busy all this time far from messy Manila, improving the lives of her constituents in concrete and tangible ways.
I think we all know who that person is, and what a compelling and positive comeback story she can offer, against the vengefulness and the sordidness of the successor who turned her office into a junk-food dispensary.